BARIATRIC-METABOLIC SURGERY
INFORMATION
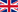
OBESITY: A DISEASE
CAUSES OF OBESITY
The genes
How well
Eating
Your surroundings
Psychological
Bariatric - Metabolic surgery: An effective tool to manage obesity

Bariatric - Metabolic surgery
Bariatric / Metabolic surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, is currently the only proven, long-term, effective tool to manage obesity. When diet and exercise have failed, as they often can, obese patients may consider bariatric surgery not only for weight loss, but also to improve or resolve many of the diseases associated with morbid obesity. Indeed, the primary purpose of bariatric surgery is to improve diseases such as type-2 diabetes, sleep apnoea, high cholesterol and high blood pressure, with a great resulting “side-effect” being weight loss.
Restriction (involving physically the reduction in the size of the usable stomach) and malabsorption (involving reduction of the caloric absorption by bypassing a portion of the small intestine) or the combination of the 2, were considered as the main mechanisms of action of the bariatric operations.
However, there is increasing evidence demonstrating that the weight loss and metabolic improvements seen following gastric bypass, mini gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy are caused by changes in gut hormones, changes in bile acid metabolism and changes in gut bacteria. Thus the new term of ‘metabolic’ surgery is now used to classify these operations. All procedures are performed laparoscopically.
The need for surgery to aid weight loss and ameliorate associated comorbidities as well as the choice of surgical procedure is dependent on discussion and assessment during initial consultation when we will provide you with expert and comprehensive advice. We strongly believe in the multidiscipline approach of each patient including assessment from the Dietician, Family Physician, Endocrinologist, Psychologist.
Bariatric - Metabolic
Surgery Options

Sleeve gastrectomy

Gastric Bypass (Roux en Y)

Mini Gastric Bypass (MGB)
Additional Info
- Metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS) is recommended for individuals with a body mass index (BMI)≥35 kg/m2, regardless of presence, absence, or severity of co-morbidities.
- MBS should be considered for individuals with metabolic disease and BMI of 30-34.9 kg/m2.
- BMI thresholds should be adjusted in the Asian population such that a BMI≥25 kg/m2 suggests clinical obesity, and individuals with BMI≥27.5 kg/m2 should be offered MBS.
- Long-term results of MBS consistently demonstrate safety and efficacy.
- Appropriately selected children and adolescents should be considered for MBS.
In June 2016, the international consensus conference “2nd Diabetes Surgery Summit, DSS-II” with the participation among others of the American diabetes association, international diabetes federation and diabetes UK, recommended bariatric surgery to patients with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 and not well controlled diabetes despite optimal medical therapy. The guidelines have been endorsed by over 50 international organisations (Metabolic Surgery in the Treatment Algorithm for Type 2 Diabetes: A Joint Statement by International Diabetes Organizations, Surgical Treatment for Diabetes Type 2 - IFSO)