LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY
INFORMATION
The word laparoscopy comes from the combination of the word laparo (lapara-abdomen in Greek) and scope (to look at , watch, in Greek)
LAPAROSCOPIC surgerypossibly
the most important development of General Surgery during the 20th century
LAPAROSCOPIC surgery
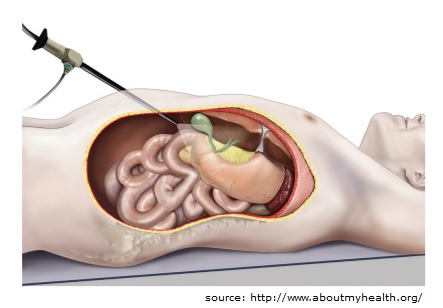
Over the last 20 years the use of this technique has expanded into almost all parts of abdominal and pelvic surgery. In traditional “open” surgery the surgeon uses a single incision to enter into the abdomen.
Laparoscopic surgery uses several 0.5-1.5 cm incisions. Each incision is called a “port.” At each port a tubular instrument known as a trocar is inserted. Specialized instruments and a special camera known as a laparoscope are passed through the trocars during the procedure. At the beginning of the procedure, the abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide (CO2) gas to provide a working and viewing space for the surgeon. The laparoscope transmits images from the abdominal cavity to high-resolution video monitor in the operating room. During the operation the surgeon watches detailed images of the abdomen on the monitor. This system allows the surgeon to perform the same operations as traditional surgery but with smaller incisions.
LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY ADVANTAGES
Smaller surgical trauma
Significantly less postoperative pain
Shorter in-hospital stay
Faster return to normal activity
Significantly reduced trauma related complications (e.g. infection, hernia, chronic pain)
Less scarring
Better aesthetic result
Additional Info
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal)
- Laparoscopic hernia repair (groin, umbilical, femoral, incisional)
- Laparoscopic appendicectomy
- Laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery
- Laparoscopic diaphragmatic hernia repair
- Laparoscopic bariatric surgery (weight loss / metabolic surgery)
- Diagnostic laparoscopy
- Laparoscopic adhesiolysis (division of scar tissue)
- Laparoscopic splenectomy
- Laparoscopic liver cyst excision or biopsy
- Laparoscopic gastric (stomach) surgery
- Laparoscopic small bowel resection (for benign or malignant conditions)
- Laparoscopic colectomy (large bowel removal for benign or malignant conditions)
- Laparoscopic Heller's myotomy (Achalasia treatment)